Low-Code/No-Code Tools Are Popular, But Untrusted
Low-code and no-code tools are making application development more convenient and flexible, but they open up organizations to security flaws. That’s according to a recent survey from Dark Reading.
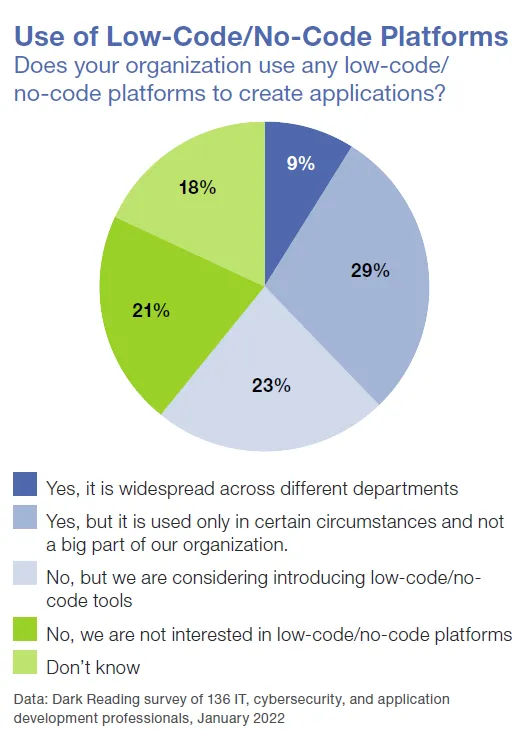
The Dark Reading 2022 Secure Applications Survey asked 136 IT and cybersecurity decision-makers about the state of application security at their workplace. While the responses showed that companies were paying more attention to application security overall, over half of the organizations (52% overall; see pie chart below) were implementing low-code/no-code in at least parts of their company.
Research firm Gartner predicts that use of low-code/no-code tools will rise from almost 25% of applications in 2020 to 70% in 2025. This is despite the serious security concerns the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) raises, including privilege escalation, data leakage, and dependency injection. Of course the security team is aware of these risks, as the Dark Reading survey shows: Only 7% of respondents say they do not have concerns about the security of applications developed with low-code/no-code tools.
The biggest concrete worry among the IT and cybersecurity personnel was the lack of oversight for how applications built with low-code/no-code tools access and use enterprise data; 32% mentioned this as a security concern. Over a quarter (26%) of respondents say they don’t trust the security of the app-building platforms, and another 26% worry that they don’t know how to even check for vulnerabilities in the low-code/no-code applications. Twenty-five percent of respondents can’t get their arms around a full catalog of these applications.
The security concern cited by the most respondents — 33% — was just “Don’t know.” That lack of clarity about where security holes might appear could be the biggest drawback of what is clearly a popular and useful technique for app development.
Download the full report here.
Read More HERE
